Today, cyberspace is the place where website thrived from technology, torture, and attack of various cyber ecstasies. Whether simple blogging or shopping online or running a multimillion corporate website, cyberattack is dangerous to such an endeavor. Types of attacks and what every owner should put into consideration as a safe site are comprehended better. Here in this blog piece, we focus on all those attacks that come to a site and see how to get rid of them.
Why Target Websites?
Cybercriminals target websites for a wide variety of reasons:
➤Monetary benefit – Customer payment information is being stolen, fraud is conducted or ransom demanded.
➤Data theft: Sensitive user data such as emails, passwords, and personal information can be incredibly valuable for identity theft purposes.
➤Damage to reputation – Competitors, or disgruntled individuals, might try to deface or damage a site.
➤Exploitation of resources – Hackers use compromised websites for sending spam, mining for cryptocurrencies, or launching further attacks.
The first measure towards cybersecurity is knowing the different types of attacks that would compromise a website.
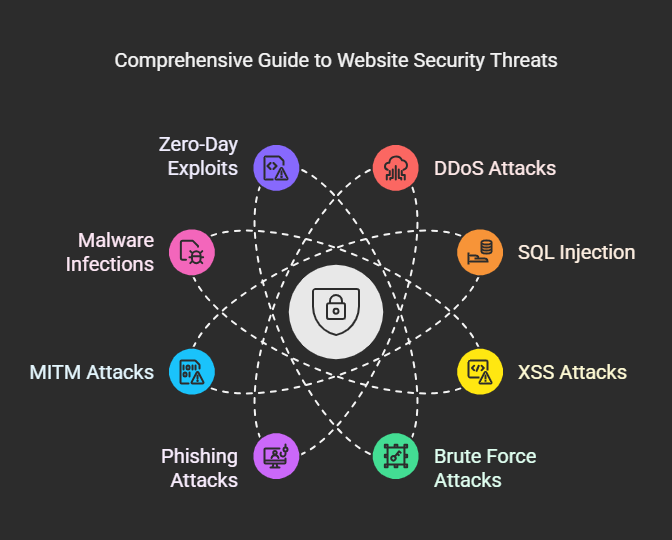
Types of Attacks a Website Can Face
1. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoSing means making a website inoperative for real users using a server through highly excessive loading of traffic;
➤Operation: Attackers use botnets (that is, a network of infected devices) to flood a site with requests overloading its bandwidth and server resources.
➤Consequences: Site downtime, loss of revenue, and damage to reputation.
➤Protection methods:
⇛ Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) such as Cloudflare.
⇛Use rate limiting and firewall rules.
⇛DDoS protection services.
2. SQL Injection (SQLi) Attacks
SQL Injection is one of the most extremely dangerous attacks a website can face, one that affects a database to exfiltrate or modify information.
➤Operation: The attackers insert a rogue SQL command through the input field (like login forms or search bars) targeting the modification or deletion of records from the database.
➤Consequences: Data breaches, the loss of sensitive information, and complete control of the database by hackers.
➤Protection methods:
⇛Use prepared statements and parameterized queries.
⇛Restrict the privileges of the connection used by the application.
⇛Ensure database system is kept up to date with the latest patches.
3. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Attacks
The XSS attacks will involve the injection of malicious scripts in web pages, which are activated on the visit of a user to the web page.
➤Operation: Attackers embed JavaScript code in the input fields of a website, which executes in the browser of a visitor.
➤Consequences: Session hijacking, phishing, and redirection to some other malicious websites.
➤Protection methods:
⇛Sanitize and validate user input.
⇛Introduce Content Security Policy (CSP).
⇛Use http-only and secure cookies.
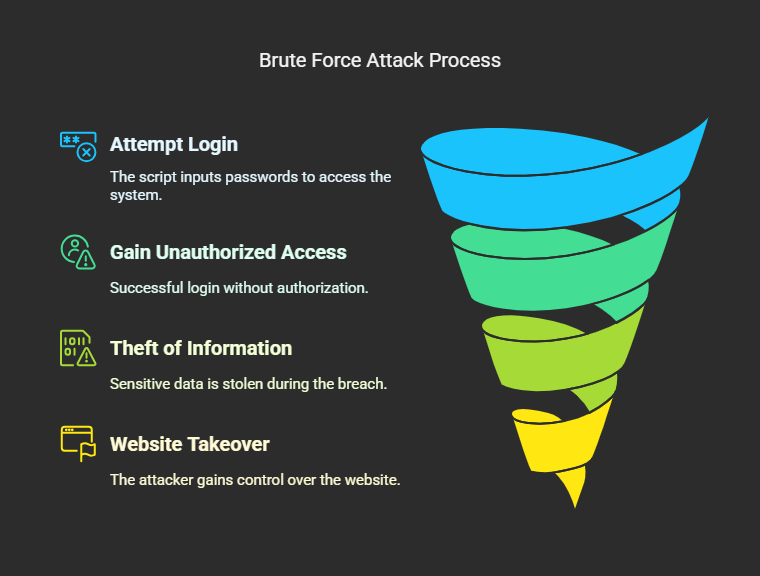
4. Brute Force Attacks
A brute force attack, in essence, goes through every possible combination of usernames and passwords in attempts of gaining access to the login thus securing the credentials.
➤Operation: An automated script will input thousands and sometimes millions of passwords until the good one is found.
➤Consequences: Access without authorization, theft of information, and taking over the website.
➤Protection methods:
⇛Have a two-factor authentication (2FA) for log-ins.
⇛Use a strong, unique password.
⇛Limit login attempts and use CAPTCHA verification.
5. Phishing Attacks
Phishing is a form of attack in which users are misled into reproducing sensitive information using malicious sites disguised as legitimate ones.
➤Operation: Attackers create illegitimate login pages, emails, or messages to retrieve credentials from users.
➤Consequences: Stealing identity, breaches of data, and financial fraud.
➤Protection methods:
⇛Use protocols for email authentication like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
⇛Have the users educated on phishing risks.
⇛Certificates of security must be updated regularly.
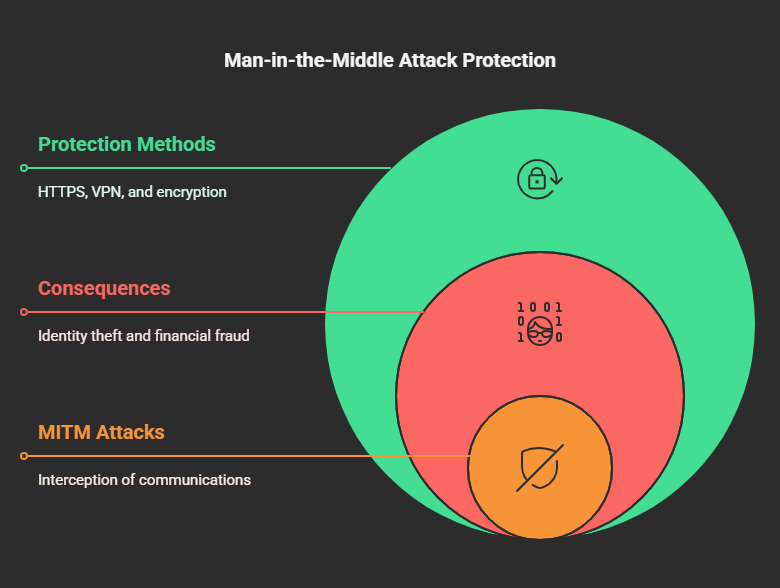
6. Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
MITM attacks are when an attacker intercepts the communications between a user and a web site.
➤Operation: Hackers go through the eavesdropping act of data transmission to gain sensitive information, such as login credentials and financial account details.
➤Consequences: Identity theft, financial fraud, and account compromise.
➤Protection methods:
⇛Use HTTPS with an SSL certificate.
⇛Refrain from public wireless LAN use without VPN.
⇛Adopt end-to-end encryption.
7. Malware Infections
Malware infections consist of the injection of nefarious software into a website to either steal data or deface the site.
➤Operation: Hackers exploit vulnerabilities to install malware capable of stealing information or rendering the website unusable.
➤Consequences: Search engine blacklisting, financial losses, and the compromise of user data.
➤Protection methods:
⇛Regular scans for malware with security plugins.
⇛Keeping the core application, plugins, and themes updated.
⇛Implementing firewalls to block suspicious traffic.
8. Zero-Day Exploits
Are targeted at unknown software vulnerabilities, as yet un-patched by the developers.
➤Operation: Find and use a vulnerability before dev’s aware of the being found.
➤Consequences: Unauthorized access, malware distribution, and compromise.
➤Protection methods:
⇛Keep the software and plugins updated.
⇛Use Web Application Firewalls (WAF).
⇛Monitor security advisories on the new threats.
9. Insider Threats
From within the organization, there are certain other instances whereby threats to security may arise.
➤Operation: Employees or contractors with access to certain sensitive systems misuse their privileges.
➤Consequences: Data leakage, sabotage, and fraud.
➤Protection methods:
⇛Access control and user monitoring of such activities must be implemented.
⇛Administrative privileges should be restricted to a bare minimum.
⇛Composition of log and audit tools.
How to Protect Your Website from Attacks
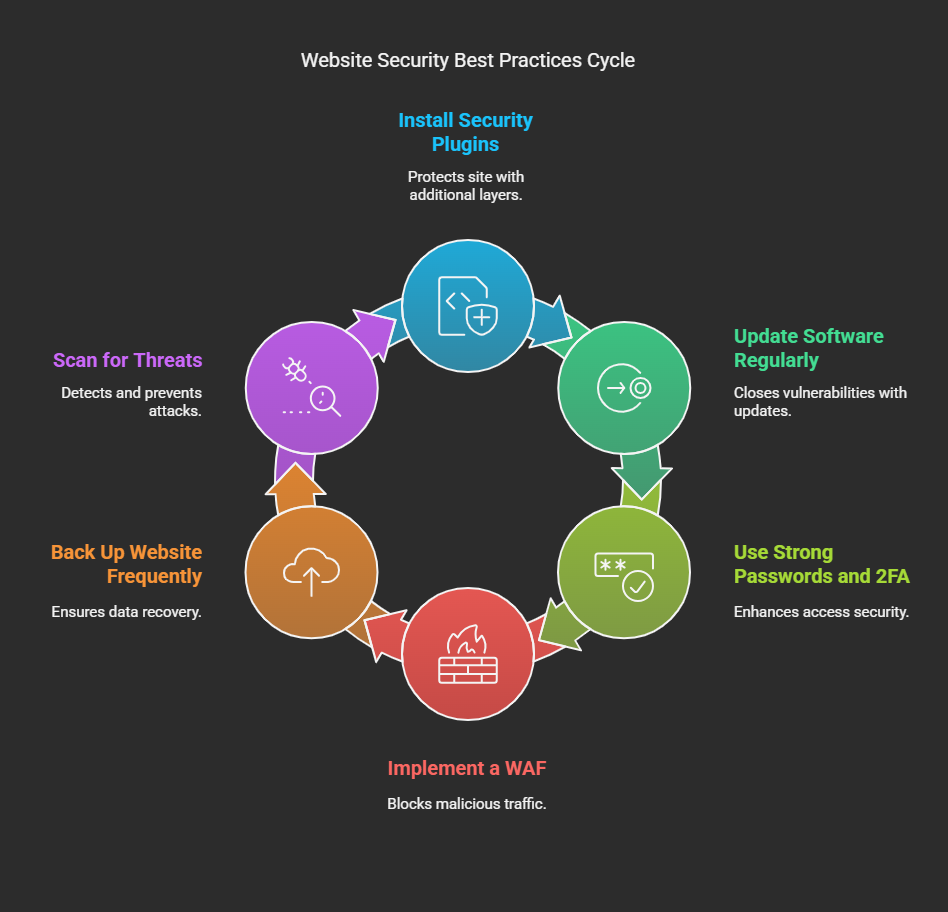
While no security measure gives 100 percent protection, adherence to these best practices can greatly reduce the defined risks:
i)Security Plugins Should Be Installed: Plugins such as Wordfence, Sucuri, or iThemes Security can deter attacks on WordPress.
ii)Update Software: Regularly apply updates to CMS, plugins, and themes and develop point security-based data for any vulnerabilities.
iii)Strong Passwords Should Be Used with 2FA: Passwords should be complex, and it is always advised to put in Two-Factor authentication.
iv)A WAF Must Be Implemented: This blocks incoming malicious traffic before it gets to your site.
v)Back Up Your Website Frequently: Keep backups in a secure location to restore it in case of an attack.
vi)Check & Scan for Threats: Security monitoring tools provide real-time tracking to detect and prevent attacks.
Conclusion:
Every day the cyber threat landscape evolves, and keeping a website secure is more important than ever. Websites can be attacked by any number of means, from brute-force methods to malware infestations or phishing scams. Knowing such threats and enforcing good security practices will protect web sites, users, and companies from cybercriminals.